Biological control of Tuta absoluta
Trichogrammas are used in biological control to manage populations of Tuta absoluta, the tomato leafminer. These predators, which are small wasps, lay their eggs inside those of the pest.
Trichogrammas against Tuta absoluta on tomato plants
Invasion of Tuta absoluta
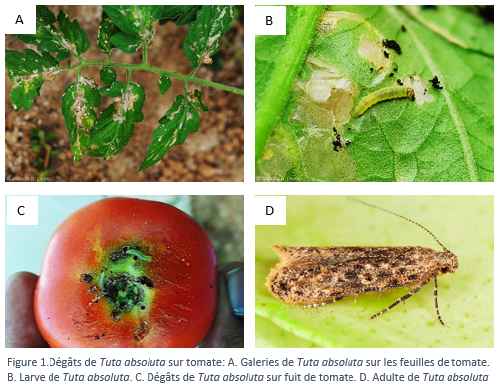
Tuta absoluta, also known as the tomato leafminer, is a small moth native to South America that has become a major pest of tomatoes and other solanaceous plants. This invasive species has posed a threat to tomato crops in Europe since its introduction to the continent in 2006[1] [2].
The larvae of Tuta absoluta attack various parts of the plant, including leaves, buds, fruits and even the tubers of the potato. Damage is more severe during the cooler parts of the day, and yield losses can affect production by 50 to 100%, especially in the absence of adequate measures.
Biological control: Trichogramma spp
Trichogramma spp is a genus of wasps comprising about 145 described species, all parasitoids of insect eggs. These wasps are generalist parasitoids, attacking a wide range of diverse host species[3]. Some species of trichogrammas, such as Trichogramma achaeae, T. euproctidis and T. evanescens, have been reported as effective egg parasitoids against Tuta absoluta[4].
Effectiveness of Trichogrammas on Tuta absoluta
Different species of trichogrammas have been tested against the tomato leafminer:
- T. pretiosum is the trichogramma most effective against T. absoluta, with a parasitism rate of 84.22%.
- T. achaeae and T. chilonis are also effective, with parasitism rates of 73.78% and 70.33%, respectively.
- T. pieridis is the least effective, with a parasitism rate of 62.56%.
Price of Trichogrammas in France
The price of trichogrammas can vary depending on the quantity purchased. For example, a batch of 4 trichogramma dispensers, sufficient for 4 weeks of action, is sold for €16.50 in France[5].
Prices may vary depending on the supplier and the quantity ordered.
Use of trichogrammas to control the tomato pest
Trichogrammas can be released both in greenhouses (limited area) and in open fields (large area) to combat the tomato pest. However, the technique used in these two environments may differ.
In open field:

In open fields, trichogrammas can be released using the integrated pest management (IPM) strategy. This strategy includes biological control agents such as Bracon hebetor (against the adult caterpillar) and trichogrammas (against eggs) combined with the use of biological preparations, pheromone traps, and judicious use of low-risk pesticides, enabling pest control with up to 90% effectiveness.
Moreover, the inclusion of biopesticides, entomophages, and pheromone traps in this integrated protection strategy for tomato plants against T. absoluta is an effective and promising initiative.
In greenhouse:

In greenhouses, trichogrammas can be released using the integrated biological protection approach. Greenhouse studies on trichogrammas combined with entomopathogenic nematodes (EPN) Heterorhabditidae and bugs such as Macrolophus pygmaeus or Nesidiocoris tenuis have shown 80 to 95% effectiveness in controlling the tomato pest T. absoluta.

Trichogrammas can be released in greenhouses using various methods, such as the use of cardboards, dispensers, or sachets. The choice of method depends on the greenhouse setup, the crop, and the target pest. Generally, cardboards containing trichogramma eggs are applied by hanging them inside the greenhouse.
Combined with the use of other predators, trichogrammas can be released immediately upon receipt. Pheromone traps can be used to catch certain species of adult leafminers to identify when they are most active inside and around the greenhouse, to better determine the optimal timing for releasing egg parasitoid trichogrammas.
(link).
How to obtain trichogramma-based products to control tomato pests?
Trichogramma-based products are marketed by various companies. These products can be applied directly in fields or greenhouses to control tomato pests.
| Product | Company | Target pest | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| TrichoCarte | MW | Tuta absoluta | €1 per card |
| TRICHOcontrol | Agrobio | Tuta absoluta | €1 per card |
| Tricholine TA | Bioline | Tuta absoluta | €1.6 per dispenser |
Trichogramma release protocol against Tuta absoluta
Here are the steps to successfully release trichogrammas against Tuta absoluta.
Preparation
Choose the right trichogramma species
There are many trichogramma species, each with specific characteristics. To combat Tuta absoluta, it is recommended to use trichogramma species specialized in parasitizing this leafminer. The most effective species against Tuta absoluta are Trichogramma brassicae, Trichogramma cacoeciae and Trichogramma evanescens[4].
Procure trichogrammas
Trichogrammas can be purchased from specialized distributors (Koppert, Biobest, Bioline…).
Store trichogrammas properly
Recommended storage conditions for trichogrammas:
- Location: A cool, dry place, protected from direct sunlight and humidity, separate from other products (pesticides, fertilizers…), clearly identified as reserved for trichogrammas.
- Temperature: 10 to 25°C.
- Humidity: 50 to 60%.
Application

Conduct regular crop inspections
Carefully monitor tomato crops for signs of Tuta absoluta infestation. Use pheromone traps to monitor the presence of adult pests and plan trichogramma releases accordingly.
Release trichogrammas at early stages of leafminer development
Trichogrammas are more effective when released before infestation. Releases should be uniform across the entire crop area to ensure homogeneous distribution of parasitoids.
- In greenhouse: Releases can be done as soon as the plants are set up. Generally, releases should be done every 15 days, from the start of the growing season until the end of the risk period for the leafminer[6].
- In open field: Releases should be done as soon as the first flights of Tuta absoluta moths are detected. Generally, releases should be done every 15 days, from the start of the growing season until the end of the risk period for the leafminer[6].
Compatibility of trichogrammas with other products
The compatibility of trichogrammas with other pesticides depends on several factors, including the type of pesticide used, its formulation, frequency of application, applied dose, and environmental conditions.
Here are some points to consider regarding trichogramma compatibility with pesticides:
Case 1: Before releasing trichogrammas
Recommendations
- Apply treatment at least 2 weeks before releasing trichogrammas to allow them to establish in the crop and start laying eggs before pests lay theirs.
- Apply the treatment uniformly over the entire crop area to ensure all pests are eliminated.
Concrete example If you want to use trichogrammas to control the tomato leafminer, it is possible to apply a treatment based on Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). This insecticide is selective and targets tomato leafminer larvae. The waiting period for this product is generally 3 days before releasing trichogrammas.
To apply this treatment, dilute the product according to the label instructions. Then use a sprayer to apply the treatment evenly over the entire crop area.
Following these recommendations maximizes the effectiveness of trichogrammas in pest control.
Case 2: After releasing trichogrammas
Recommendations
- Choose a selective pesticide that targets only the pests to be controlled to spare beneficial insects like trichogrammas.
- Carefully read the product label before use to know the pesticide type, dose, and waiting period.
- Respect the waiting period indicated on the product label to allow trichogrammas to develop and mature.
- Monitor the crop carefully after treatment application to detect any signs of pesticide toxicity on trichogrammas.
Concrete example If trichogrammas have been released to control the tomato leafminer and a treatment against aphids is needed, use a biological insecticide based on Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). This pesticide is selective and targets aphids. The waiting period for this product is generally 3 days.
To apply this treatment, dilute the pesticide according to label instructions. Then use a sprayer to apply the treatment evenly over the entire crop area. It is important to respect the 3-day waiting period before harvesting the crop.
Continuous monitoring
Continue monitoring the effectiveness of trichogrammas by regularly examining plants for the presence of Tuta absoluta eggs.
Repeat if necessary
If needed, perform additional releases depending on the infestation development.
Tips
- Perform additional releases if the population of Tuta absoluta is high.
- Combine trichogramma releases with other control methods against Tuta absoluta, such as using pheromone traps or biopesticides.
References
- Adilkhankyzy A, Alpysbayeva KA, Nurmanov B, Naimanova BZ, Bashkarayev NA, Kenzhegaliev AM, et al. Integrated Protection of Tomato Crops against Tuta absoluta in Open Ground Conditions in the South-East Part of Kazakhstan. OnLine J Biol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;22(4):539–48.
- Adly D, Nouh GM. Impact of combined releases of the egg parasitoid, Trichogramma euproctidis (Girault) and the entomopathogenic nematode, Heterorhabditis bacteriophora to control Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) in tomato greenhouses in Egypt. Egypt J Biol Pest Control. 2019 Dec 17;29(1):91.
- Application Areas – AMW Nützlinge [Internet]. [cited 2023 Nov 23]. Available from: https://www.amwnuetzlinge.de/en/products/trichokarte/
- Agrobio - Biological pest control and natural pollination [Internet]. [cited 2023 Nov 22]. Available from: https://www.agrobio.es/products/pest-control/trichocontrol-trichogramma-achaeae-caterpillar-control/?lang=en
- Chailleux A, Biondi A, Han P, Tabone E, Desneux N. Suitability of the Pest-Plant System <I>Tuta absoluta</I> (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae)-Tomato for <I>Trichogramma</I> (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) Parasitoids and Insights for Biological Control. J Econ Entomol. 2013 Dec 1;106(6):2310–21.
- Firouz KABIRI, BIOTOP, A success story against Ostrinia nubilalis, in maize crops, and now against Tuta absoluta in tomato crops, ABIM, Lucerne 2009
- Entomology and Nematology Department, UF/IFAS Extension.DOI: doi.org/10.32473/edis-IN1382-2022
- El-Sayed, A., El-Sherif, A., & El-Sherif, A. (2022). Efficacy of Trichogramma euproctidis and Heterorhabditis bacteriophora in controlling Tuta absoluta in tomato greenhouses in Egypt. Journal of Entomological Research, 46(1), 1-10.
- Schäfer L, Herz A. Suitability of European Trichogramma Species as Biocontrol Agents against the Tomato Leaf Miner Tuta absoluta. Insects. 2020 Jun 8;11(6):357. doi: 10.3390/insects11060357. PMID: 32521821; PMCID: PMC7349915.
- Tricholine TA – the new approach of controlling Tuta Absoluta « Bioline [Internet]. [cited 2023 Dec 3]. Available from: https://www.biolineagrosciences.com/2018/09/17/tricholine-tuta-the-new-approach-of-controlling-tuta-absoluta/
- Shawer et al., 2021. Impact of cold storage durations on Trichogramma evanescens (Westwood) (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) during their nymphal stage. PubMed Central. doi : 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.08.014
- Almeida Raul Porfirio et Cruz Ivan. 2013. Production technology of Trichogramma spp. for biological control of lepidopteran pests.
- ↑ Bloem, S. and E. Spaltenstein. 2011. New Pest Response Guidelines: Tomato Leafminer (Tuta absoluta). USDA–APHIS–PPQ–EDP Emergency Management, Riverdale, Maryland.
- ↑ Anonymous1, CABI Invasive Species Compendium. Tuta absoluta. Visited 22 November 2023, https://www.cabi.org/isc/tuta
- ↑ Wael Elwakil, Ethan Doherty, and Adam Dale, 2022. “TRICHOGRAMMA WASPS TRICHOGRAMMA SPP. (INSECTA: HYMENOPTERA: TRICHOGRAMMATIDAE)”
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mir Jalil Hejazi , Shahzad Iranipour Mehdi Arzanlou , Antonio Biondi, Nicolas Desneux.2021. Lethal and sublethal effects of synthetic insecticides and bio-insecticides on Trichogramma brassicae parasitizing Tuta absoluta. PubMed Central. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243334
- ↑ https://www.insectosphere.fr/trichogrammes-anti-mites-textiles
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Gaspar Legendre, Maurane Buradino, Yannie Trottin, Jean-Michel Leyre, Véronique Baffert, et al. 2020 . Study of the efficacy of different trichogramma strains against Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) in experimental greenhouses. AFPP - Tenth International Conference on Agricultural Pests, French Association for Plant Protection (AFPP).


