Regenerative agriculture

For 10,000 years some practices in agriculture have caused a progressive decrease in the vegetation of a territory and in the organic matter (OM) of soils, which results in :
- decreased precipitation,
- loss of biomass production capacity,
- loss of vegetation,
- soil erosion .
Thus, lush areas or moorlands have been transformed into deserts. But the good news is that we can reverse this through regenerative agriculture. Indeed, agriculture is the most powerful lever to reverse climate change as long as its trajectory regenerates the ecosystem, taking care of soil richness, preserving biodiversity, keeping lands covered, and restarting the virtuous water cycle.
Regenerative agriculture allows the production of healthy food : soil health ensures human health.
Definition

The goal of regenerative agriculture is to reproduce vegetation, a water cycle, crops, economic activity in rural territories and progressively restock carbon in soils. To improve degraded soils, it will take about fifty years, provided the management allows regeneration. For example, it is necessary to avoid putting a herd in young plantations to prevent buds from being eaten or to think about protecting them well from animals.
The objective is to restart the natural soil cycles (mycorrhiza, earthworms,...).
Principles

- It is an agriculture that preserves instead of degrading. Agriculture in general degrades because it burns more carbon than it leaves in soils. Due to significant mineralization and soil work, soils gradually deteriorate, respond less well to water excess, and erode.
- Regenerative agriculture is an agriculture that improves the environment, having a positive impact on carbon dynamics in soils, the water cycle, biodiversity, and thus brings health to plates.
- To practice regenerative agriculture, there is a dimension of resilience of the farm and risk management against hazards. To limit these risks, it is necessary to have several productions on the farm which will provide some economic security before environmental security. This economic security will be based on diversity and not on highly specialized production.

This implies that there will often be a livestock component associated with crop production crops components. There must be complementarity between these components but they must be quite different in terms of species grown (avoid wheat/barley which are too similar). Livestock is not mandatory but it helps to close the fertility loop because it allows organic return to the plot of what would have been exported as crops.
- One must design flows around farms as biomass transforming into kg of nitrogen. For example, if 100 t of corn are sold from a farm, if these 100 t are eaten by chickens, how much nitrogen but also potassium, phosphorus, magnesium does it represent? One must be aware of how much the soil is depleted by practices.
What is the dry matter flow going out and coming into/on the farm and what is the impact of practices on soil mineralization, how much biomass is produced? Performing a humus balance is useful.
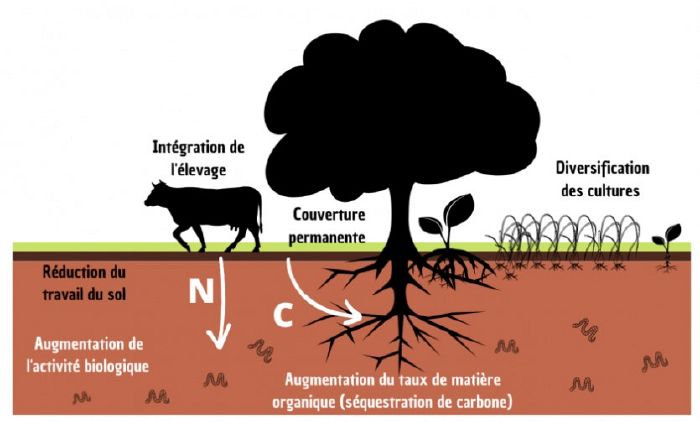
Implementing regenerative agriculture
Implementing regenerative agriculture on a farm is a revolution of the system. Before starting, it is necessary to have a plan and follow its different steps :
- Training is the sine qua non condition before starting, because ecosystem regeneration is complex and errors can be numerous without basic knowledge, which could lead to discouragement and backtracking. Training organizations can be Chambers of Agriculture, alternative associations, CIVAM,...
- Being accompanied and supported, finding people willing to work with us on the subject : technician, neighbors, family to comfort oneself in risk-taking.
- Testing on small areas to appropriate different technical itineraries (ITK). It is possible to start with service provision or borrow equipment to avoid large investments. Later, equipment can be purchased individually or through CUMA.
- Measuring the impact of practices will allow evaluating if what has been implemented is going in the right direction or not. Several parameters can be monitored such as humification coefficient (K1), mineralization (K2), agricultural practices, soil working depth, stone content, bulk density, soil type, residues on soil, weather,...
- Stabilizing technical itineraries once well established and aiming for cost reduction.
- Sharing experience to encourage others to try!
Measuring stored carbon quantities
To measure carbon storage, there are indicators (Regeneration index, Indiciades, Agroecology flower...) and organizations capable of valorizing environmental externalities, i.e., able to finance carbon under certain conditions.
For example, to claim Carbon Credit, a farmer must prove that thanks to their practices, there is :
- Additionality : the farmer makes efforts and gains something extra.
- Permanence : efforts made will last as long as possible.
- Reliability : methods and measurements.
If the farmer can prove these, they can generate carbon credits that can be bought by companies needing to offset their CO2 emissions. That is why the quality of Carbon Credits, i.e., their reality and the relevance of methodologies, is essential for buyers.
Many methodologies exist to calculate stored carbon quantities. They rely on modeling performance, precise measurements of some performance elements, mapping, or spatialization to varying degrees.
How to assess different methodologies?
| Measurement rigor | Additionality | Permanence | Control /
Transparency of data |
Methodology
precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-quality direct sampling,
confirmed by models |
Reflects real market
trends |
Period > 100 years
+ buffer pool and/or insurance instrument |
Third-party control of
different steps and transparent data securely stored |
+++ |
| Models calibrated or
parameterized with some samples |
Not sufficiently
based on real-world data |
Period > 10 years
+ buffer pool and/or insurance instrument |
Third-party control
of different steps |
++ |
| Models not parameterized
by sampling or samples with a weak sampling plan |
No additionality test | Period < 10 years, no
buffer pool, no insurance |
Self-control,
classic database |
+ |
Agriculture has benefits beyond carbon

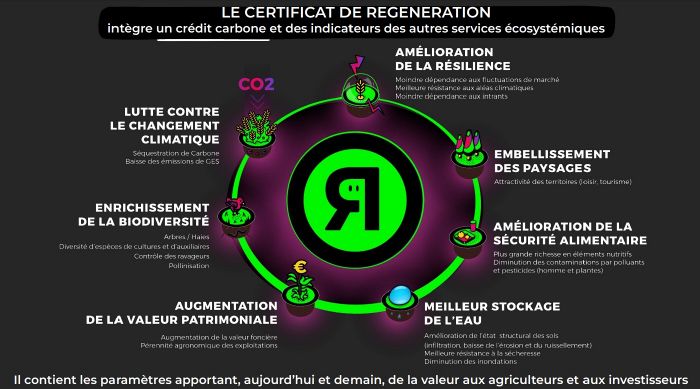
Regenerative agriculture also positively impacts other externalities such as :
- Water resource : availability, infiltration, flood risk.
- Biodiversity.
- Agroecological infrastructures.
- Climate change mitigation.
- Food security.
There is a regeneration certificate established by Regeneration. This certificate considers the Carbon Credit but also indicators of other ecosystem services :
Necessary equipment

- The first thing to equip oneself with is knowledge. One must train, learn new techniques, generate maximum biomass, build systems that grow the most plants. This requires curiosity and training on various topics such as managed grazing, fertilization localization, reduced tillage, CA, cover crops, agroforestry, optimizing performance related to plants, everything that makes more plants grow on the same unit area with less fertilizer and everything that helps learn to reduce soil work.
- For field crops : specific equipment is needed to limit soil work such as a no-till seeder and tools to localize fertilizers (organic or mineral) as much as possible on seed rows.
- For livestock: a quad, stakes. Investments are lower.
Expected results
- Reduction of operating costs : it depends on the starting point. For example, Félix Noblia of Larrous Farm reduced operating costs by 30% in 2 years by consuming less diesel and fertilizer and having fewer mechanization expenses.
- Time saving : ⅓ less time in the tractor on field crops, but more time in the fields observing.
Advantages and limits
Advantages
- Significant improvement of several dimensions of the agricultural ecosystem, such as soil structure (water retention) and biology (better mineral accessibility).
- Income security thanks to diversification of components.
- Additional income if eligible for Carbon Credit.
- Reduction of operating costs.
- Applicable to all types of production, and at different levels of involvement : meaning one does not have to practice conservation agriculture in organic farming to claim regenerative agriculture. There are different levels of success without always going further. No tillage, covering soils, and managing fertilization are already very important points.
Limits
Technical itineraries are long to implement, many errors are made at the beginning such as :
- Not localizing fertilizers properly.
- Thinking soil compaction cannot be undone because of no-till (one should not hesitate to decompact if necessary).
- Not having a pragmatic approach to what happens and not having a fair assessment of problems.
Another limit is that the vague definition of regenerative agriculture allows anyone to claim it, with more or less justification and with more or less clear intentions. For more info on this aspect, you can consult this page.
Summary
The summary of regenerative agriculture could be this phrase : "Before I suffered a bad context and bad choices (but that was agriculture as it was 15 years ago), now if I fail it is my mistakes because I am the one testing and taking the risk of failing. My greatest success is always managing to progress technically and learn." Félix Noblia.
Aid
- For agricultural machinery : PCAE (Competitiveness and Adaptation Plan for Agricultural Holdings) at the regions level, via CUMA it is also interesting.
- For training : the VIVEA fund via MSA.
- For practice change : the CAP and its conditionalities on MAEC (Agri-environmental and climate measures).
- For Carbon Credit : private companies within their CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) approach.
Valorization of products from regenerative agriculture
Products from regenerative agriculture are not yet valorized.
Advice before starting
- Train!
- Start small with tests before changing the whole system at once.
- Have funds to start because the transition from a damaged system to a regenerating system is complicated. Experimentation costs time, seeds, equipment, knowledge restitution.
- It takes between 3 and 5 years to succeed, but it depends on the starting point. For example, to switch from tillage to CA, it takes about 5 years to appropriate the itineraries.
- Do not persist stubbornly if it does not work, one must adapt. Poor human judgments cause failure to adapt properly to hazards and strategies implemented.
Prebiotics
Soil prebiotics (fungi and/or bacteria) can be a catalyst, but the best remains to do cover crops and regenerative agriculture.
They remain interesting because they can bring benefits to very degraded ecosystems where so much flora has been lost that reintroducing exogenous flora can help regenerate soils. What fits the context will develop, the rest will not survive, natural selection applies.
Generally, they will have beneficial impacts, but everything depends on the initial state of the ecosystem.
Regenerative agriculture and the water cycle
The more vegetation on a territory, the more it rains. It is important to do more than the neighbor because there will always be more water where there is more vegetation.
Vegetation acts as a buffer for temperatures and helps better manage water cycles, infiltration. Irrigation should be considered occasionally but with the goal of vegetation and not exclusively agricultural production.
Conclusion
Regenerative agriculture is a reinvention of the agricultural model, we face a revolution. We all realize that on the climate and food security fronts, things are at the end of a cycle and this regenerative agriculture offers hope for a future.
Further reading
Interested in the work of :
Sources
This page was written thanks to the kind contribution of Félix Noblia.
Cette technique s'applique aux cultures suivantes
La technique permet de favoriser la présence des auxiliaires et bioagresseurs suivants
La technique est complémentaire des techniques suivantes
La technique est incompatible avec les techniques suivantes
Cette technique utilise le matériel suivants
Cette technique fait référence aux outils d'aide à la décision suivants
- ↑ What is a carbon credit in agriculture. Paysage in Marciac 2022, Félix Noblia. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P_jA5Z-9T4o