Practicing biological control using trichogrammas
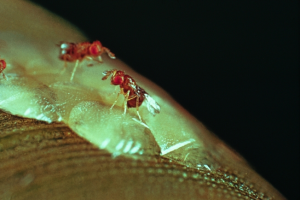
This technique consists of introducing trichograms (Trichogramma brassicae, micro-wasp parasitoids contained in cardboard supports) into the field at a date based on temperature sums. The trichograms must be introduced every year because they do not survive the winter in large numbers. Against the first generation of European corn borer, 100,000 to 215,000 wasps/ha are released from 25 to 50 different points. If used against the second generation, 250,000 to 600,000 wasps per hectare must be released at 50 points.
Example of implementation : In Burgundy (only one generation of European corn borer) : place the trichogram supports at the appropriate period (Plant Health Bulletin, etc.): 25 placement points per hectare.
Implementation period On established crop
Spatial scale of implementation Plot
Application of the technique to...
All crops : Not generalizable
On corn only (all types: grain, silage, sweet, seed).
All soil types : Easily generalizable
All climatic contexts : Easily generalizable
Regulations
POSITIVE influence
This technique is the subject of a CEPP (Certificate of Phytopharmaceutical Product Savings) action no. 2017-006 / Controlling European corn borer by releasing trichograms.
Another action concerns the use of trichograms in vineyard : 2017-024 / Controlling grapevine moths by releasing trichograms.
Marketing Authorization
Effects on the sustainability of the cropping system
Environmental criteria
Effect on air quality : Increasing
acidification : DECREASE
phytosanitary emissions : DECREASE
GHG emissions : DECREASE
particulate emissions : DECREASE
Effect on water quality : Increasing
N.P. : DECREASE
pesticides : DECREASE
turbidity : DECREASE
Effect on fossil resource consumption : Decreasing
fossil energy consumption : DECREASE
Other : No effect (neutral)
Reduction, insofar as the insecticides used represented a risk of water pollution. This is not the main risk related to insecticides against the European corn borer.
Placement is done manually.
Biodiversity: Increase
The insecticides mainly used against the European corn borer (oxadiazines, pyrethroids, and organophosphates) have effects on non-target arthropods, notably on beneficials and bees.
Biodiversity: no effect (neutral)
Trichograms parasitize very few eggs of non-target insects and exert limited competition against native parasites. Most trichograms die after oviposition. The supports used to introduce them into fields are biodegradable cardboard.
Agronomic criteria
Productivity : No effect (neutral)
Soil fertility : No effect (neutral)
Soil fauna and microorganisms develop better and therefore potentially better fulfill their functions related to soil fertility.
Water stress : No effect (neutral)
Functional biodiversity : Increasing
Reduced use of insecticides allows better development of many species useful to agriculture, particularly insects (biological control, soil aeration, organic matter transformation, pollination, etc.).
Other agronomic criteria : Decreasing
Reduced risk of insecticide resistance.
Economic criteria
Operating costs : Increasing
35 to 40 euros per hectare and 3 to 5 ha per hour per person for control of the first generation and 45 to 55 euros per hectare and 2 to 3 ha per hour per person for the second.
Mechanization costs : Decreasing
Placement is done manually.
Margin : Increasing
Other economic criteria : Decreasing
Fuel consumption: Decrease
Placement is done manually.
Social criteria
Working time : Decreasing
Peak period : Increasing
Between 2 and 5 ha treated per hour per person, which is higher than the time needed for chemical treatments.
Effect on farmer health : Decreasing
Insecticides are dangerous for users, so using trichograms reduces health risk.
Observation time : No effect (neutral)
Placement periods can be known via plant health bulletins.
For more information
- Trichograms
- -Biotop
Biotop, beneficials production company, Website, 2012
- Non-chemical control of European corn borer using trichograms or Bt corn
- -Meissle M., Bigler F., Mouron P. (Agroscope ART, Switzerland); Kabiri F. Biotop, France); Pons X. (Universitat de Lleida, Spain)
ENDURE. From theory to practice. Case study on corn - guide number 1, Technical brochure, 2010
- Monitoring and protection against corn borers
- -AGPM
AGPM - technical info no. 393, April 2010, Technical brochure, 2010
Keywords
Bioaggressor control method : Biological control
Mode of action : Catch-up
Type of strategy regarding pesticide use : Substitution
Sources
- Julien Halska (INRA) - Dijon (21) - julien.halska@grignon.inra.fr