Streptomyces
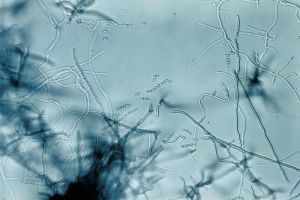
To be completed. The genus Streptomyces refers to non-pathogenic Gram-positive filamentous bacteria belonging to the order Actinomycetes, which includes the genera Mycobacterium, Corynebacterium, Nocardia, Rhodococcus and Frankia.
The genus Streptomyces was characterised by Selman Waksman (1888-1973) and Arthur Trautwein Henrici (1889-1943) in 1943. These bacteria are mainly found in the surface layers of soils, where their mycelial growth and ability to sporulate facilitate their development and dispersal. Streptomyces are saprophytic bacteria, growing by degrading organic matter in the soil using numerous extra-cellular hydrolytic enzymes, thus playing an active role in the formation of humus.
Streptomyces are bacteria of major interest, both industrially and in terms of fundamental research, as they have a development cycle that is unique among prokaryotes and are responsible for the production of a large number of bioactive molecules, notably antibiotics. Streptomyces avidinii, in particular, produces a molecule with a high affinity for vitamin B8, streptavidin.()