Sitona lineatus
1. General description
| Scientific name | Sitona lineatus |
| Classification | Order Coleoptera, family Curculionidae |
| Geographical range | All of France, with a preferred area south of the Rennes-Lyon diagonal (Rhône-Alpes, PACA, South-West, Poitou-Charentes, Grand Ouest, Berry). |
| Crops affected | Pulses(alfalfa, peas, beans, clover, vetch, beans, birdsfoot trefoil, lentils, etc.) |
2. Biology and epidemiology
Biological cycle
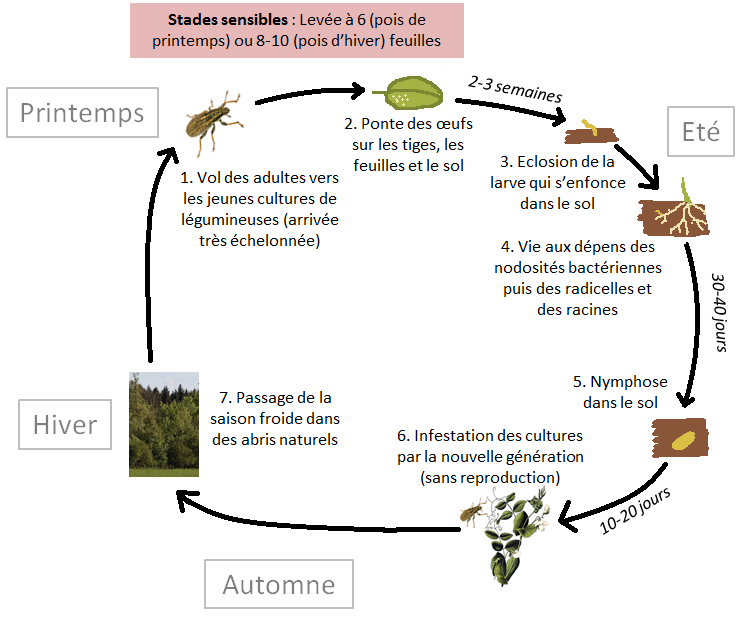
Conditions favourable to development
| Environment | In shallow soils, the damage caused by sitones is often exacerbated by drought in April-May, which reduces the number of nodules. |
| Climate | Mild, dry winters are favourable.
|
| Cultivation history of the plot | Early emergence of spring seedlings is favourable to sitones. |
| Plot environment | Areas with fallow land or leguminous crops and hedged farmland are favourable to sitones. |
3. Damage
Symptoms and damage
The semi-circular notches made by adults on the edges of leaves do not have a major impact on yield, unlike the larvae, which disrupt the nitrogen supply of crops by feeding on nodules and roots.
The risk is more frequent on spring peas than on winter peas, and the pea weevil, when it has a choice, clearly prefers faba beans to other crops.
Measuring systems
For peas, the intervention threshold is a total of 5 to 10 notches on the first leaves.
For lentils, according to the Haute-Loire Chamber of Agriculture, the damage threshold is 50% of plants with one or more bites out of 20 plants sampled.
Nuisiblity
(to be completed)
4. Management methods
Measures upstream of the crop
For lentils, it has been observed that nodule damage is greater in early-sown plots, so late sowing could help to reduce escape damage. In addition, as sitones emerge from the soil after overwintering, a longer rotation may reduce the likelihood of effective recolonisation and hence plot infestation. However, sitones are capable of flying considerable distances, so a plot can also be infested by adults from further afield.
Catch-up solutions
| Type | Description | Effectiveness |
| Chemical control | See list of approved products on the Terres Inovia website (references) | Control is only effective if the adults are affected before oviposition (6-leaf stage in spring peas, 8-10 leaves in winter peas). |
Innovative solutions
/
5. To find out more...
| Title | Type of document | Year | Authors | Publishers | Précisions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ephytia page : pea leaf spot | Website | / | INRA | INRA | link vers le site |
| ABAA database : pea weevil | Website | 2017 | EcophytoPIC | ACTA | link to the website |
| Herbea : pea weevil | Website | 2017 | Solagro | Solagro | link to the website |
| Pea Sitone | Website | 2017 | Arvalis | Arvalis | link vers le site |
| Sitone on peas | Website | 2017 | Terres Inovia | Terres Inovia | link to the website |
| The 5 lentil pests | Technical brochure | / | Haute-Loire Chamber of Agriculture, Puy Green Lentil Producers' Group | Haute-Loire Chamber of Agriculture | brochures |
| Lentil, an ancient crop for modern times. | Book | 2007 | P. Sevenson, M. Dhillon, H. Sharma, M. El Bouhssini | Springer Netherlands | Chapter 20 : Insect pests of lentil and their management (pp 331-348) |
Annexes
S'attaque aux cultures
