Kakothrips pisivorus
1. General description
| Scientific name | Frankiniella robusta (syn. Kakothrips robustus, Kakothrips pisivorus) |
| Classification | Order Thysanoptera, family Thripidae |
| Geographical range | In all pea crops in Europe. In France, thrips proliferate mainly in spring pea fields in the northern half of the country. |
| Crops affected | Springpeas, spring broad beans, broad beans, cultivated and wild legumes, wild mustard, poppies, viperina, etc. |
2. Biology and epidemiology
Biological cycle
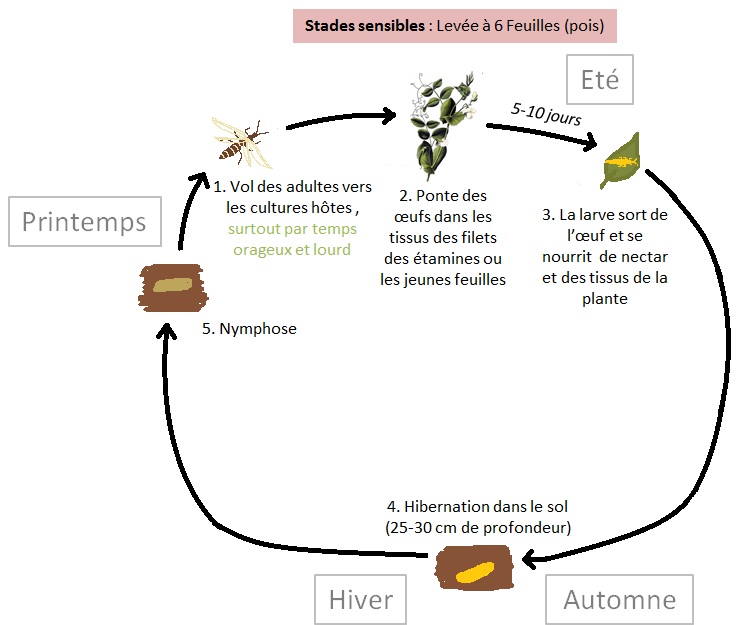
Conditions favourable to development
| Environment | |
| Climate | Adult flight occurs mainly in stormy, heavy weather, and outbreaks are favoured by hot, dry weather in early summer. Heavy rainfall decimates populations. |
| Cultivation history of the plot | For peas, thrips is more damaging on vegetable crops than on field crops. |
| Plot environment |
3. Damage
Symptoms and damage
By gradually emptying the cells, the larvae weaken the shoots. The plants are puny and dwarfed, very branched, with embossed and brown-stained leaves. Inflorescences shrivel up or remain sterile. Young pods dry out, while older ones are abnormally curved, with shiny silvery parts dotted with brown woody spots.
Measuring systems
For peas, the control threshold is 20 larvae or eggs per 10 flowers.
For faba beans, the control threshold is 2 individuals per flower.
Pests
For peas, the presence of 250 eggs per 10 inflorescences causes a reduction in the pea harvest of up to 60%.
4. Management methods
Pre-crop measures
Since Thrips overwinters in the soil, a rational rotation is favourable.
For peas, late sowings and late varieties are particularly at risk. Early cultivation and the choice of early varieties is important.
For lentils, it is important toremove volunteer soya shoots that have been reported as sources of thrips infestation.
Catch-up solutions
| Type | Description | Effectiveness |
| Biological control | The predatorybug (Orius laevigatus) is a natural enemy of thrips, which appears spontaneously in glasshouses in the south of France in July andAugust. It is widely used in crop protection throughout the year in France. | |
| Chemical control | (to be completed) |
Innovative solutions
/
5. To find out more...
| Title | Type of document | Year | Authors | Publishers | Précisions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e-phytia page : Pea thrips | Website | 2017 | INRA | INRA | link vers le site |
| ABAA database : pea thrips | Website | 2017 | EcophytoPIC | ACTA | link to the website |
| Page herbea : Pea thrips | Website | 2017 | Solagro | Solagro | link to website Information on crop and landscape management that may favour the predatory bug. |
| Lentil, an ancient crop for modern times | Book | 2007 | P. Sevenson, M. Dhillon, H. Sharma, M. El Bouhssini | Springer Netherlands | Chapter 20 : Insect pests of lentil and their management (pp 331-348) |
Annexes
S'attaque aux cultures