Implementing Agroforestry Systems

Agroforestry helps to meet various objectives: each agroforestry system is multifunctional. The design of an agroforestry system allows favoring one or another function, depending on the pursued objectives.
Types of systems
A variety of agroforestry systems can be integrated into the agricultural landscape.
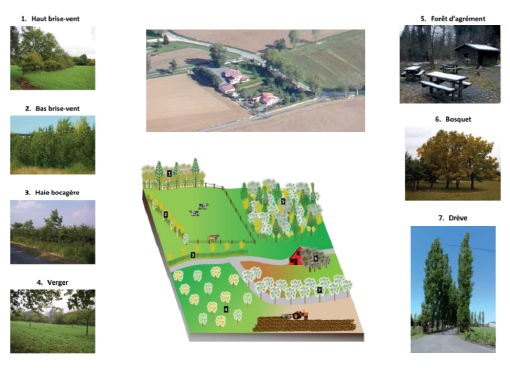
Isolated trees
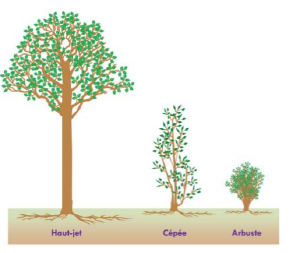
High-stem trees
High-stem trees are trees whose trunk can easily reach 30m in height.
Coppices
These are groups of shoots developing on the stump of a coppiced tree (cut 10-20cm above the ground). The height of these trees ranges between 6 and 15m.
Shrubs
Shrubs generally have a height less than 7m.
Grouped trees

Clumps
These are trees forming a small area group, less than 5 ares.
Groves
These are trees forming a medium-sized group, between 5 and 50 ares.
Trees in open field
Coppice stands
Coppice stands are groups of trees with short rotation (10 years on average).
Woodlands on farmland
Aligned trees
Rows
These are trees planted in one or two rows, most often in pure stands.
Avenues
Avenues are trees planted most often on both sides of a road, often in pure stands and at fixed spacing.
Agroforestry edges
Agroforestry edges are located at the border of a forest massif, ideally composed of several forest layers and consisting of a herbaceous fringe, a shrub belt, and a tree layer.
Linear coppices
Linear coppices are plantations in one or several rows of trees regularly harvested (every 5 or 10 years).
Associated trees
Low trimmed hedges
These are trees or shrubs planted in one or several rows, trimmed to less than 3m in height and narrow width, often monospecific.
Free hedges
Hedges free hedges are composed of mixed trees, occasionally maintained, every 10 to 20 years.
Windbreaks
Hedges windbreaks are a particular form of tall hedge, very vertically structured, combining high-stem trees, coppices, and shrubs to provide protection against wind for crops or animals.
Wooded strips
Wooded strips are a particular form of multi-row tall hedge, with variable width up to 10m.
Orchards
Orchards are often located near the main place of farming activity.
Hedgerows
Hedgerows are networks of hedges or rows of trees marking the boundaries of plots of unequal size and different shapes: large windbreaks oriented north-south, small windbreaks oriented east-west.
Functions of systems
- Production of quality wood
- Production of woody biomass
- Production of edible berries
- Production of fruits or nuts
- Protection of infrastructures
- Protection of animals
- Protection of crops
- Soil protection
- Water protection
- Air protection
- Increase of biodiversity
- Landscape enhancement
Sources
Appendices and links
Est complémentaire des leviers
- Practicing agroforestry
- Implementing agroforestry systems
- Practicing gentle vine pruning
- Pollard pruning
- Practicing full grass cover in vineyards
- Planting hedges
- Inter-row grass cover in vineyards
S'applique aux cultures suivantes
Défavorise les bioagresseurs suivants