Chemical weeding
 Weed management using chemical plant protection products
Weed management using chemical plant protection products
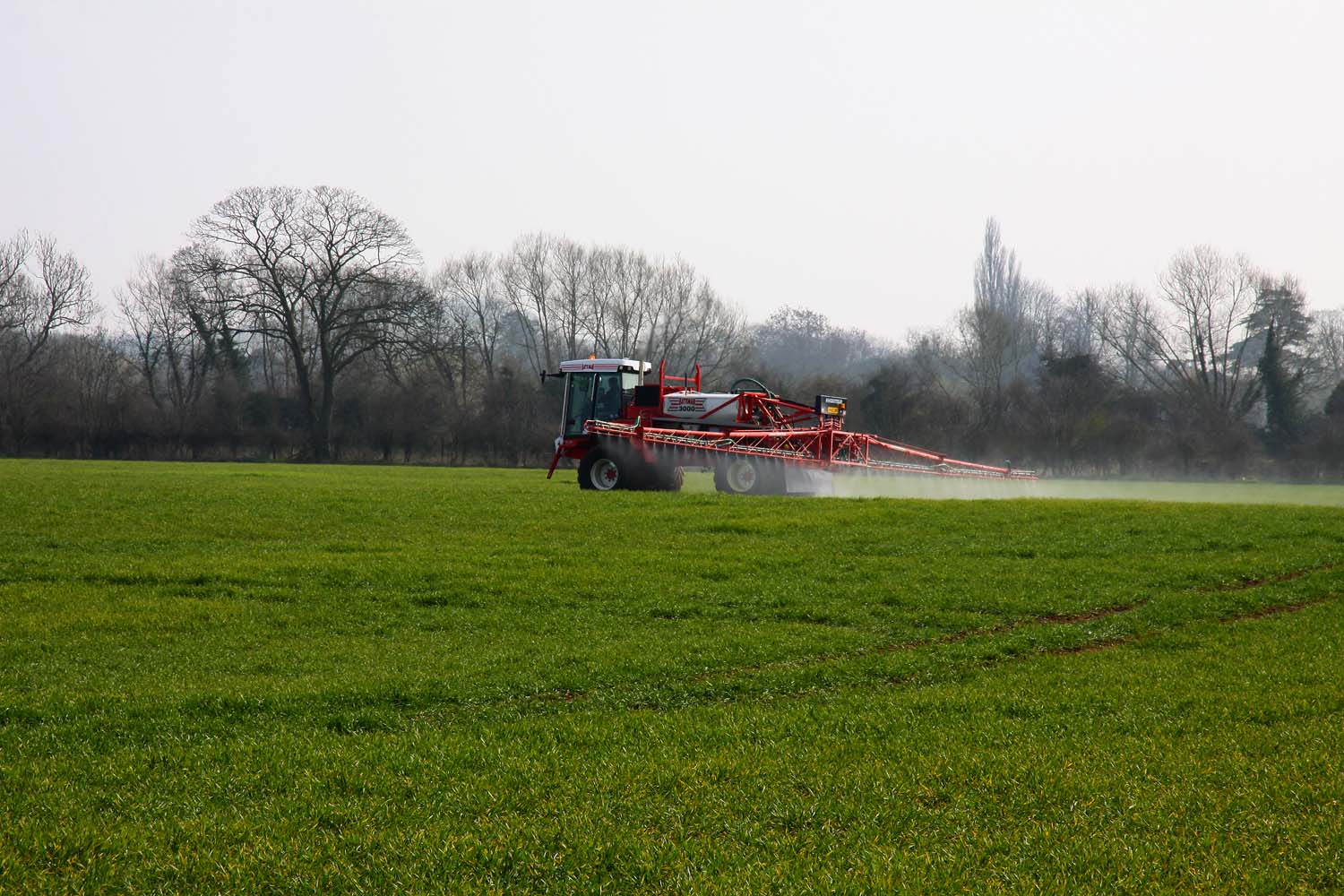

Chemicalweed control involves applying a herbicide to weeds to eliminate them because they compete with cultivated plants.
Effectiveness of herbicides
Theeffectiveness of herbicides depends on a number of parameters (soil and climate conditions, type and quantity of weeds, etc.). These parameters will greatly influence the action of herbicides on weeds and therefore their performance.
For greater effectiveness and greater respect for the environment, it is necessary toadapt and optimise the use of herbicides by playing on different factors.
Choice of herbicide
First of all, it is important to choose a herbicide that is suited to the weeds present in the field, taking into account their potential resistance and phenology. You therefore need to take into account :
- The weed species present.
- The degree of weed infestation, i.e. the more weeds there are, the dirtier the plot.
- Weed emergence period, emergence depth, etc., in order to adapt solutions and/or application periods.
- Weed resistance.
Technical itinerary
Thetechnical itinerary (ITK) also plays an important role inherbicide selection andeffectiveness. The action of herbicides depends in particular on :
- The following crop : some herbicides are very persistent, which means that the molecules can remain in the soil until the following crop is planted and have a toxic effect on it.
- The phytotoxicity of the herbicide : it is important to choose a herbicide that is non-toxic to the current crop, so that only weeds are targeted.
- Timing of herbicide application : the herbicide can be applied pre-emergence or post-emergence. post-emergence.
Application conditions
The various application conditions must also be taken into account to ensure maximum effectiveness of the herbicide product. The main conditions to take into account are :
- Soil and weather conditions (humidity, wind, temperature, soil moisture, etc.).
- The preparation of the spray mixture (formulation, order of addition of components, pH of the water, agitation, etc.), which can affect the herbicide's effectiveness by 30 to 50%.
- Dosage.
- Equipment (nozzles, forward speed, etc.).
- Low volume : volume of spray mixture less than 100 litres/ha.
How herbicides work
There are different types of herbicide, depending mainly on their composition and how they work.
The types of application will therefore differ :
- Root-penetrating herbicides are applied directly to the soil as a pre-emergence treatment.
- Foliar-penetrating herbicides are applied to the leaves as a post-emergence treatment.
As well as the types of action :
- Contact herbicides, which act after penetrating the tissues, but without migrating to other organs of the plant.
- Systemic herbicides, which act after penetration and can migrate from one part of the plant to another.
Preventive herbicide ?
Many people use a herbicide as insurance against risk, but it is wiser to use herbicides as the last stage in a weed control strategy. Certain preventive methods (before weeds appear) make it possible to avoid invasion by weeds without the need for curative treatments (after weeds have appeared) :
- Treat the edges of plots.
- Know the weed and its annual decline rate.
- Stagger sowing dates.
- False seeding, etc.
THE IFT
The Treatment Frequency Indicator (TFI) corresponds to the number of doses of plant protection products applied per hectare during a crop year.
It is based on the number of doses of product applied per hectare over the course of the season (seed treatments, herbicides, insecticides, etc.).
| Type of IFT | Description |
|---|---|
| Herbicide IFT | Weed destruction |
| IFT insecticides | Control of insects, mites and nematodes |
| IFT fungicides | Control of fungi |
| Other TFIs | Growth regulators, molluscicides, rodenticides, bactericides and virucides |
| IFT seed treatments | Seed protection |
| IFT biocontrol | Macro-organisms, micro-organisms, chemical mediators, natural substances |
The IFT is measured using the formula :
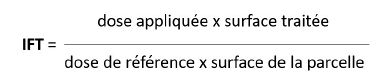
The reference doses correspond to the approved doses.