Building a Motor Cultivator Retrofit
This document introduces the conversion of a thermal tiller with a power of 6-8 hp into an electric tiller with a power of 5 kW. It allows understanding the architecture and design principles that enable the realization of each of the technical sub-assemblies composing the retrofit as well as the final assembly of the tiller-Re.
This document describes the approach and particular points of the architecture and design, approach and particular points that cannot be specified on the technical drawings for:
- The architecture and design points of the tiller-Re
- Other constructive alternatives than those presented in the technical drawings
Important note:' The technical drawing file comes from a prototype built without plans. The prototype determined the feasibility and operational qualities of such a retrofit. The technical documents have not yet been confirmed in all details and all dimensions indicated in the technical file. The realization must take into account some potential assembly complements and tolerances even if MEEED has done its best to avoid them. MEEED cannot be held responsible for this.
The conversion of a thermal tiller via a retrofit into an electric tiller is done by replacing the thermal engine and its accessories with an "Electric Block". This electric block is attached in place of the thermal engine after removing the clutch, if there is one at that location.
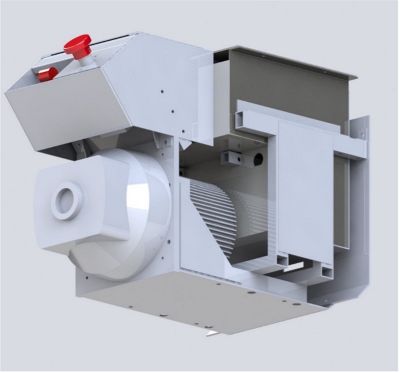
Preamble 1
The retrofit of the Tiller-Re was designed:
- To adapt to different brands and types of tillers. This adaptation is done by the "Link Plate" between the "Electric Block" and the output shaft of the gearbox after removing the clutch, of course if there is one at that location.
- Each machine having a different gearbox output typology, the linking elements between the electric motor shaft and the gearbox output shaft must be studied and adapted for each machine. The link plate will also be adapted in size and centering for each machine.
- The linking system implemented on the prototype and adapted to a GOLDONI tiller is as follows:
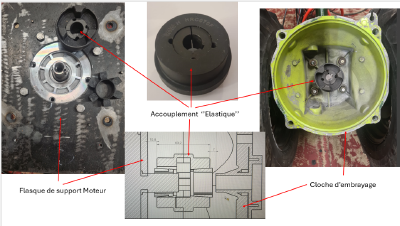
Note: As shown by the mechanical diagram above and depending on the retrofitted tiller model, the reduction of the length of the gearbox output shaft must be carried out precisely (+/- 1 min) respecting the dimension chain represented by:
- The length of the electric motor shaft.
- The length of the coupling (equipped with its functional play between flanges)
- The length of the gearbox output shaft
In case of incompatibility between shaft diameter / inner diameter of the coupling sleeve, the use of a lathe may become necessary. In the specific case of the retrofit carried out, the standard coupling was compatible.
Preamble 2
The proposed retrofit of the tiller-Re was designed:
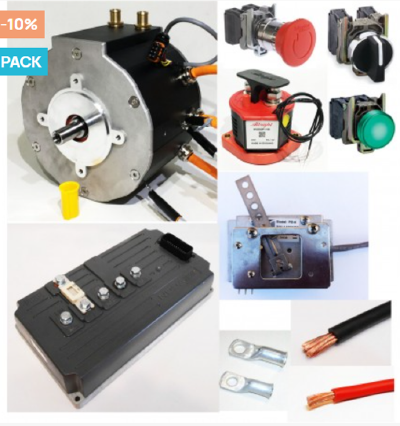
- On the Electric Kit from Kit Elec Shop built around the ME1719 motor: the components have specific dimensions and installation constraints which are those of the technical file.
- On the prismatic modules available from NKON of 100A ref.: REPT CB56 This prismatic module has dimensions (height 119 mm Width 148.4 mm, thickness 52.32 mm) which are those of the technical file.
The design was made based on the physical dimensions and technical characteristics of these components. Any alteration in the choice of the kit and prismatic modules may lead to a partial or total redesign.

The Electric Block
The design manufactures a compact "Electric Block" supporting all the electrical components of the retrofit conversion of a thermal tiller. There is no need to modify the structure of the original thermal tiller's gearbox. The "Link Plate" and the "coupling" of the "Motor Block" ensure the connection between the electric motor and the gearbox.
The "Electric Block" is complete and functional by itself. It can be validated without the presence of the gearbox and its coupling.
The "Electric Block" consists of the following modules:
Note: The "Front skid" can receive the charger if it is decided to install it permanently. It will be installed in the upper position and the "Front skid" will be drilled.
Note: The mechanism for holding and articulating the hood, if installed, will be fixed on the front skid. The elements of this fixation are not described in the file.
The electrical circuitry
The electrical circuitry is imposed by the kit. There are no alternatives to realize it differently. The tools required for the realization of the electrical circuitry are:
- Large wire cutters or shears for 25 mm² power cables,
- Standard electrical wire cutters for control wires from 0.2 to 2 mm²
- Mechanical or hydraulic crimping pliers for tubular terminals from 15 mm² to 50 mm²
- Crimping pliers for low voltage cable terminals from 1 to 3 mm
- Heat gun for installing shrink tubing
- Electrical protective gloves
- Multimeter
Required skills: The required skills are mainly on
- Crimping terminals on cables
- Understanding the risk of short circuit and thus fire on the battery pack or one of the 16 installed prismatic modules.
Note: any modification or work on the power electrical system must be carried out with maximum safety principle. The battery cutoff switch offers a disconnection of the battery via its + pole and allows work downstream while maintaining the required precautions to avoid touching the wiring upstream of the cutoff switch.
Maximum safety consists in disconnecting the battery fuse and having the cutoff switch open.
The electrical diagram
The electrical diagram is centered on the SEVCOM controller, the key piece of the electrical system. The controller has on its front face 3 connection zones:

- Battery connection via 2 screw terminals B+ and B– marked on the module. The B+ terminal is associated with a fuse protecting the controller.
- Motor connection via 3 screw terminals M1, M2, and M3 marked on the module.
- The positioning of wires M1, M2, and M3 determines the rotation direction of the motor. If it is found that the motor does not turn in the correct direction, then 2 terminals must be swapped.
- Connection of control and safety devices. This connection is concentrated on a single connector. Most wires from this connector are pre-wired by the Kit supplier. They have at their ends the control or safety devices that are their functions. Only the following wires are unassigned and will need to be made:
- Wires for the dead man's safety control
- A pair of wires whose function is safety-related and will not be used in this retrofit (possibility to use this contact for additional safety if desired)
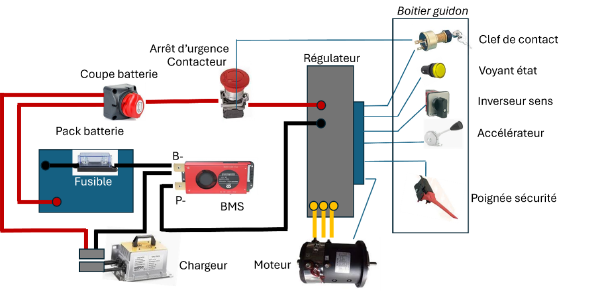
Note: it is important to familiarize yourself and identify each function coming from the multi-wire connector.
List of components to add to the kit
As a reminder, the Kit from Kit Elec is quite complete. It is supplied with the following accessories:
- Ignition key
- Status indicator light
- Direction reversal button
- Emergency stop / Switch
- Accelerator mechanism
The following components must be added as necessary to realize the entire electrical diagram for the Tiller-Re:
- The BMS or battery management system: It is an essential safety and management device for the prismatic battery modules. It performs the following three functions:
- Safety by measuring currents and cutting off the battery if the called currents exceed the set thresholds.
- Quality of charging of each prismatic battery module via balancing wires connected to each prismatic module.
- Reading charge levels, voltage of each prismatic battery module with associated alarms if a too large imbalance is measured.

The recommended BMS is a model from the DALY brand. It communicates via Wifi through an application available for smartphones. It is via the application that positioning parameters and operational limits with alarms are established. The BMS manual should be read carefully to master this component and set parameters adapted to the tiller-Re. Most factory default parameters are suitable. Parameters to be handled are:
- Maximum discharge current
- Voltage level of prismatic modules: default setting in Life Po
For monitoring the state of the prismatic modules, each module is connected to the BMS by a cable connected to one of the poles. Due to this large number of cables and their required short lengths, the BMS is installed on the "Battery Pack". See the battery manufacturing chapter. The balancing cable passages are planned in the "Battery box".
- The battery cutoff switch 12-48v 275 amperes as shown in the image below:

The cutoff switch allows electrically separating the battery via its + pole from the rest of the electronics. Its use is mainly useful during long storage or when it is desired to avoid an unintended and involuntary start of the motor.
Note: any modification or work on the power electrical system must be carried out with maximum safety principle. The cutoff switch offers a disconnection of the battery via its + pole and allows work downstream while maintaining the required precautions to avoid touching the wiring upstream of the cutoff switch. Maximum safety consists in disconnecting the battery fuse and having the cutoff switch open.
- The handlebar box: The handlebar box receives the following control devices

- Ignition key
- Operation status indicator light
- Electric motor rotation direction switch
- Accelerator mechanism installed inside the box
- The dead man's safety handle: for example ref. DEB5539 from NHP Motoculture

The handle is a regulatory and essential safety device. It is electrically connected to the controller. It ensures the so-called dead man's safety, i.e., when not engaged or released, it prohibits any motor operation or stops it if it was engaged. The dead man's safety handle is to be fixed to the left handlebar grip.
- Accelerator handle with cable
The accelerator handle must be mechanically coupled with the accelerator mechanism provided in the Kit. The cable is to be connected to the metal lever of the provided mechanism. The sheath and cable must be adapted to the positioning of the handlebar box.




- LifePO4 charger: The charger is what allows charging the "Battery Pack". The charger must be a charger with specifications adapted to the "Battery Pack". Either a charger for 16S in LifePO4 and a charging current of 28 to 30 amperes. It should be waterproof if possible.

The charging connector is of the ANDERSON 50A type. This connector has the particularity of being symmetrical with polarization keying. This means that the Male and Female connectors are identical while respecting the polarization of the connection.
Power wiring
The kit is supplied with lengths of 25 mm² power cables colored red for cables that will be positive poles or +, and black for negative poles or -. It is also supplied with the tubular terminals necessary to make the various junctions. These cables must be cut to the correct lengths and finished with terminals adapted to the terminals (6 or 8 mm), depending on the components and the needs of the assembly below:
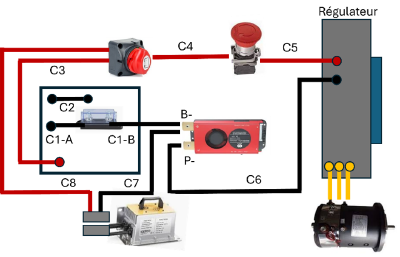
- C1-A: black battery – cable: this cable connects the – terminal of the battery to the fuse of the Battery Pack. Length:
- C1-B: black battery - cable: this cable connects the battery fuse to the BMS on the B- terminal
- C2: black cable connecting the – pole of all prismatic modules installed in the upper compartment to the + terminal of all prismatic modules installed in the lower compartment (see assembly plans of the "Battery Pack")
- C3: red + cable: this cable is connected to the last + pole of the series of 16 prismatic modules. It exits on the rear face of the "Battery Pack" to be connected to the cutoff switch
- C4: red + cable: this cable connects the "Cutoff switch" to the switch/punch within the "Controller block" sub-assembly
- C5: red + cable: this cable connects the switch/punch to the + pole of the controller.
- C6: black - cable: this cable connects the P- pole of the BMS to the – pole of the controller
- C7: black – cable from the BMS on the – pole and C8: red + cable from the cutoff switch form an Anderson-type connection point for the battery charger. The length of these cables and the positioning of the Anderson connector will be a choice depending on the placement of the charger, on-board or external to the tiller-Re
Wiring of control and safety devices
The kit is complete regarding wiring needs for control and safety devices. All control and safety wires are on a single connector at the SEVCON controller.
Some wires will be too long. Their length can be adapted by cutting and making a new junction.
Mechanical construction of the "Electric Block"
There certainly exist other ways to design the Tiller-Re, based on the built prototype, a technical file was made and detailed plans were issued. This technical file is sufficiently complete to allow the construction of an electric retrofit without having to establish new design plans or additional detailed plans (except alternatives).
Note: Within this technical file, the plans named REF-XXX-A0 describe the parts that make up the sub-assemblies of the Tiller-Re construction. For example, for some parts like the "Battery box" REF-001-A0, if all dimensions are specified, the construction method of the box is not specified. It will be up to each person, depending on available tools and skills, to select the construction method they decide. These methods are called "alternatives". When the alternative is not specified, the nomenclature of these plans ends with A0.
The technical file consists of:
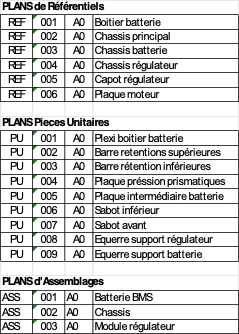
- Reference plans or REF XXX A0. They contain detailed sub-assemblies dimensioned on their critical dimensions. Construction of the different parts is based on these reference plans and mounting alternatives are possible.
- Unit part plans or PU XXX A0. These plans describe some simple parts without alternatives.
- Assembly plans or ASS XXX A0. These plans indicate particular assembly criteria of the technical sub-assemblies. They assist in the construction of the retrofit and aim to avoid assembly errors.
Material requirements
The design of the technical file for the reference plans requires widely available materials:
- Rectangular steel tube 30x20x2 mm
- Steel metal bracket 25x25x2 if an assembly technique requiring them is chosen
- Steel or stainless steel plate 2 mm thick:
- On some sub-assemblies, aluminum is a suitable substitute material
- Square aluminum bar 20x20x2 mm
- Hex head stainless steel screw-nut M6 70 mm length: pack of 10
- Hex head stainless steel screw-nut M6 45 mm length: pack of 20
- Stainless steel spring washer or Grower washer for 6mm screws: 30
- M6 stud 45 mm length for: 10 (can be cut if necessary)
- Countersunk head screw-nut M6 15 mm length: quantity depending on bracket assembly method
- Alternative rivet for bracket assemblies
Note: Some parts have dimensions that could be more suitable but would require a wider supply of materials. It is therefore recommended to build with these dimensions.
Note: The selected screws are M6 screws generalized over all assemblies. Some screws will need to be adapted in length if necessary.
Technical alternatives
The technical dossier does not intend to cover all possible technical alternatives for the construction and assembly of the various components of the "Electric Block". It provides the dimensions to be respected for each component. It allows technical alternatives that do not require specialized tools but tools generally available in most workshops:
- Tube cutting
- Flat sheet metal cutting
- Angle grinder or grinder
- Drill press
- Electric welding station
- Riveting pliers
- Standard toolbox with wrenches and screwdrivers
The skills required in the mechanical construction of the components of the Motoculteur-Re are
- Good practice of arc welding or TIG
- If riveting, the selection, implementation, and construction dimensioning by rivet.
Note: An alternative to arc welding or TIG is spot welding. Many assemblies between sheets with 90° folds allow the use of this technique.
The dimensions indicated in the technical dossier are those of the finished product to be respected. Possible alternatives have been considered within the proposed dimensions, and therefore these dimensions should not require modifications to implement them.
The following sub-assemblies are mainly concerned by these technical alternatives:
- Battery box REF-001-A0
- Regulator chassis REF-004-A0
- Regulator cover REF-005-A0
Note: Flat and bent parts can be sourced from companies that cut and form parts on demand. Such sourcing avoids all cutting and forming work while supplying just the needed raw material. For information:
Note: This sourcing requires defining an assembly technique for the flat and bent parts according to the dimensioning.
Technical alternative 1: assembly by welding
Assembly by welding is a simple and solid technique for mounting flat or bent sheets. To weld two sheet metal plates at a right angle, you can follow these general steps:
Preparation of parts: Ensure that the edges of the plates are clean and free of rust or dirt. You can use a wire brush or solvent to clean the surfaces.
Positioning: Place the two sheet metal plates so that they form a right angle. You can use clamps or pliers to hold the parts in place.
Welding: Use a suitable welding station (for example, a MIG/MAG or TIG welder) to perform the weld. Start by welding the corners to fix the plates together, then gradually fill the joint.
Finishing: Once the welding is finished, let it cool. You can then grind or sand the weld to obtain a smooth finish.

Note: A metal square will be extensively used to properly position the sheets to be welded and respect the dimensions of the finished product to be made.
Note: Where necessary, metal squares (25x25x2mm) are an alternative to edge-to-edge welding. These squares will position and structure flat weld beads and thus avoid performing edge-to-edge welds, which can sometimes be complicated if the sheets are not perfectly flat and well cut.
Technical alternative 2: assembly by countersunk screw
Assembly by screw is a simple and solid technique for mounting flat or bent sheets. Where necessary, metal squares (25x25x2mm) will position and structure the drill holes. The countersunk heads will be positioned to avoid creating protrusions where they are to be avoided (inside the battery box) and elsewhere for aesthetic reasons (regulator chassis and regulator cover).
Technical alternative 3: assembly by rivet
Assembly by rivet is a simple and solid technique for mounting flat or bent sheets. Where necessary, metal squares (25x25x2mm) will position and structure the rivet drill holes. The rivet heads will be positioned either to avoid protrusions (inside the battery box) or for aesthetic reasons (regulator chassis and regulator cover).
Pop rivets, also called blind rivets, are commonly used to assemble sheet metal parts when access to the back of the assembly is limited or impossible. Here are the general steps to perform sheet metal assembly by pop rivet:
Preparation of parts: Ensure that the sheet surfaces are clean and free of dirt or rust. Align the sheet parts so that they are correctly positioned for assembly.
Drilling: Use a drill to make holes in the sheets at the locations where you want to place the rivets. The hole diameter must correspond to the diameter of the rivets you use.
Insertion of the rivet: Insert the rivet into the hole, ensuring that the rivet head is on the visible side of the assembly.
Use of the riveter: Place the riveting tool (riveter) on the rivet stem and squeeze the riveter handle. This will pull the rivet stem, deforming the opposite end to form a back head, thus fastening the sheets together.
Breaking the stem: Continue squeezing the riveter until the rivet stem breaks, indicating that the rivet is properly installed.
Verification: Inspect the rivet to ensure it is well fixed and that the sheets are securely assembled.
Additional dossiers: Assemblies
Assemblies of the "Battery Pack"
The "Battery Pack" is a key part of the Motoculteur-Re. A dedicated assembly technical dossier is provided.
Important note: the construction of the "Battery Pack" requires many precautions. Indeed, a short circuit of one of the prismatic batteries, even very brief, can cause a fire of the batteries. This fire cannot be stopped by any extinguisher. It is self-sustained by the battery's raw materials. Therefore, all precautions will be taken to avoid such an incident. In particular, the workspace for assembling the "Battery Pack" will be cleared and kept away from other flammable materials. Wearing protective gloves is strongly recommended.
The recommended steps for assembling the "Battery Pack" are indicated in the "Battery Pack" assembly dossier.
Assembly of the "regulator module"
To properly mechanically assemble the 3 components on the metal support before wiring, ensure that everything fits well and make corrections if necessary:
- The regulator is fixed by 4 screws 6 mm length 35 mm
- The circuit breaker is fixed with the supplied screws
- The push button is fixed with the supplied screws
The proposed assembly steps are:
- Mount the regulator on the support
- Do not yet mount the circuit breaker and push button and before that:
- Set the circuit breaker to the open position (green) and fix on the circuit breaker
- The cables C3 and C8 together on the same terminal
- The cable C4
- Set the circuit breaker to the open position (green) and fix on the circuit breaker
- Fix on the push button the cable C4 coming from the circuit breaker
- Attention point: the two terminals of the push button, which are the start command, must be visible on the side opposite the regulator support
- Fix on the push button the cable C5 going to the + pole of the regulator
- Fix the circuit breaker and the push button by passing the cables through the openings provided for this and indicated in the assembly plan
Assembly of the handlebar box
The handlebar box houses the regulator controls
- Drill the cover to the dimensions of the controls
- Install the electrical controls
- Make the cable connection of bicycle type, between the throttle grip and the electrical acceleration control, installed inside the box



The handlebar box must be chosen to accept all components to be installed, including the throttle control, which is quite substantial. This throttle control has the return spring and is complete in its functions. It includes the rest end-of-travel switch which performs motor braking as required in the programming document.
Source
From Technical dossier: Architecture and Design,
Maraichage Efficient in Water and Decarbonized Energy or MEEED - Motoculteur-Re
MEEED / Les hameaux du soleil – Cyprès N°1 / 06270 / Villeneuve Loubet / Tel 06 24 39 57 67




