Acyrthosiphon pisum
1. General description
| Scientific name | Acyrthosiphon pisum (syn. Macrosiphum pisum or Acyrthosiphon onobrychis) |
| Classification | Order Homoptera, family Aphididae |
| Geographical range | Very common in France |
| Crops affected | Cycle completed entirely on legumes(sainfoin, alfalfa, trefoil, vetch, peas, beans, lentils, clover, etc.), perennial species allowing infestation of annual species. |
2. Biology and epidemiology
Biological cycle
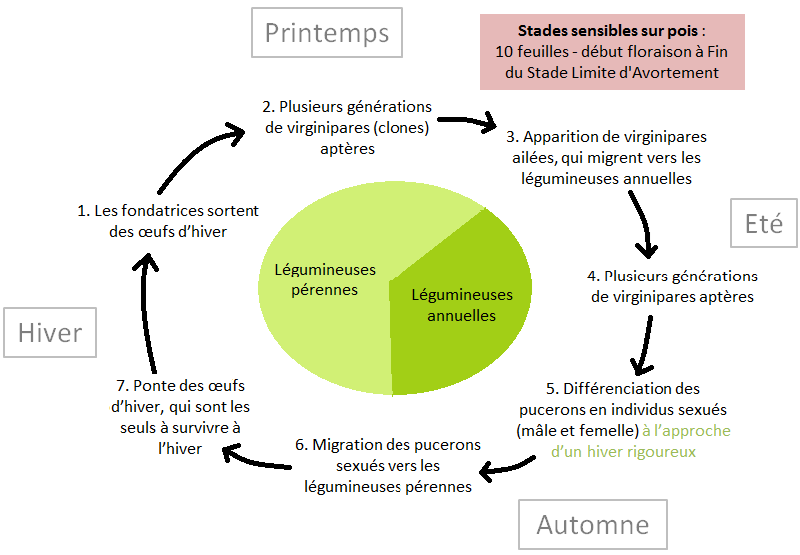
Conditions favourable to development
| Environment | |
| Climate | A mild winter favours the early arrival of aphids on peas.
|
| Cultivation history of the plot | |
| Environment of the plot |
3. Damage
Symptoms and damage
The aphid can cause two types of damage by colonising the stems, leaves, flowers and pods of a plant :
- Direct damage, due either to the development of saprophytic fungi (dull black felting) on the honeydew produced by the aphid, or to the stings that the aphid makes on the plant to feed on sap and which weaken the plant (abortion of flowers, reduction in the number of pods and PMG, opening of pods).
- Indirect damage linked to the transmission of several viruses that the aphid vectors.
Measuring systems
When the pea reaches the sensitive stages, place a stiff white sheet under the vegetation and shake the stems (the aphids will drop off). Repeat the operation several times. According to Arvalis - Institut du végétal, control is always profitable when the population reaches the threshold of 30 individuals per stem.
Pest
(to be completed)
4. Management methods
Measures upstream of the crop
Early sowing of peas would make it possible to shift the plant's sensitive stages with respect to the aphid's biological cycle (but unreliable information according to Herbea, see references).
Catch-up solutions
| Type | Description | Effectiveness |
| Biological control | Certain ladybirds, parasitic wasps and birds regulate aphid populations. | Limited impact, rate of predation and parasitism unknown. |
| Chemical control | Several products are authorised. It is important to choose a product that is specific to aphids and that respects pea beneficials. | Good, unless a pyrethroid is used on its own. Beware of bee legislation during flowering or exudate production! |
Innovative solutions
/
5. To go further...
| Title | Type of document | Year | Authors | Publishers | Details |
| ephytia page : green or pink pea aphid | Website | 2017 | INRA | INRA | link vers le site |
| ABAA database : green pea aphid | Website | 2017 | EcophytoPIC | ACTA | link to the website |
| Green aphid on pea | Website | 2017 | Terres Inovia | Terres Inovia | link to the website |
| Green pea aphid | Website | 2017 | Arvalis | Arvalis | link to the website |
| Encyclop'Aphid - the aphid encyclopedia - A. pisum | Website | 2017 | Evelyne Turpeau, Maurice Hullé, Bernard Chaubet | INRA | link to the website |
| Herbea leaflet - green pea aphid | Website | 2014 | Solagro | Solagro | link to the website |
Annexes
S'attaque aux cultures
Favorise la présence des bioagresseurs
